Very important for batteries, incorrect charging methods can overcharge or undercharge the battery, affecting the performance and life of the battery. The two most common charging methods are as follows:
A. Constant voltage charging
For valve-regulated lead-acid batteries, this charging method is the best charging method. The control charging voltage is related to the ambient temperature and the battery's operating mode.
Secondary battery charging: 2.23 ~2.30/volt per cell, at 25℃,
Battery charging for repeated use: 2.40 to 2.50/cell, at 25℃.
Note: The maximum starting charging current is generally set to not exceed 0.3 CA.
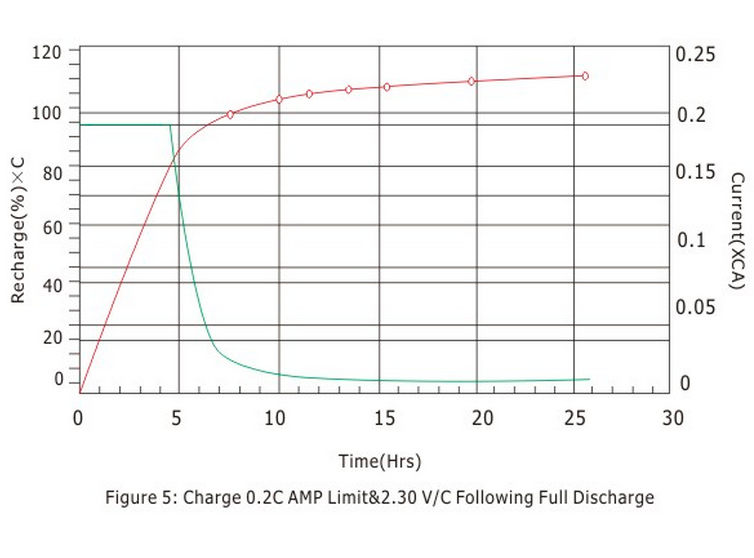
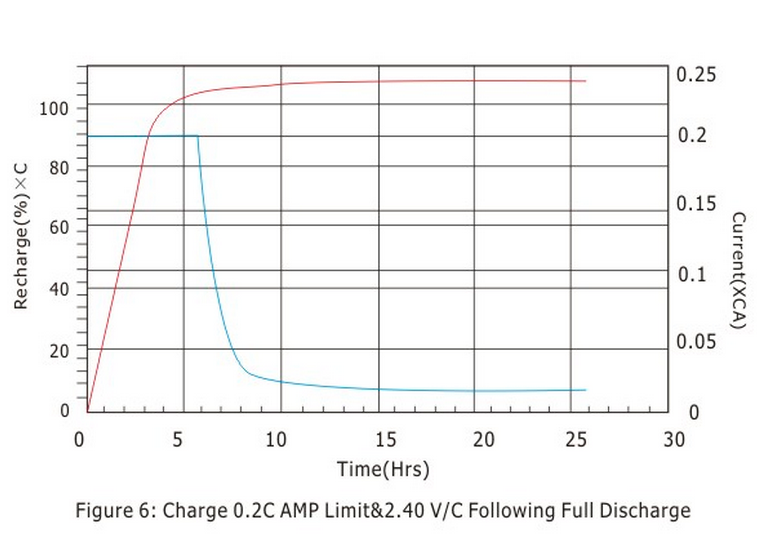
(Fig. 5, 6) are the charging curves of the battery, from which it can be seen that when the charging voltage of the battery is 2.30V/cell at 25℃, the charging current drops to 0.5~4mA/AH when the battery is fully charged and remains unchanged. When the battery is charged to 2.40V/cell, the charging current drops to 3~10MA/AH when the battery is fully charged and remains unchanged.
B. Constant current charging
When using this method to charge the battery, it is important to immediately cut off the charging power source when the battery is fully charged, otherwise, it can cause overcharging of the battery, which can damage the battery performance and life. When using constant current charging, the charging current is generally not greater than 0.1CA, and the battery is considered fully charged when the charging capacity reaches 1.07~1.15 times the previous battery discharge capacity.
Effect of temperature on battery charging voltage: As the chemical reaction speeds up with the increase in temperature and slows down with the decrease in temperature.
Charging time
For spare batteries, the time required to recharge a battery after it has been powered is generally not less than 24h. For batteries that are to be cycled, if the previous discharge capacity and the initial charging current are known, the charging time required at an ambient temperature of 25℃ can be calculated from the following formula.
Note: Tch = charging time required for the battery to be fully charged (hr)
Cdis = The amount of charge (ampere hours) that has been discharged from the battery since the last time it was charged.
I = Maximum Initial Charging Current (Ampere)